
Powerful Single Node K3s on Hetzner for CHEAP!
Single-Node Kubernetes Series
- Powerful Single Node RKE2 on Hetzner for CHEAP! (Part 1)
- Powerful Single Node K3S on Hetzner for CHEAP! (Part 1a)
- Powerful Single Node K3s on Hetzner for CHEAP! (Part 2)
The K3s Cluster
No, your eyes do not deceive you. This is a very similarly named blog to our Powerful Single Node RKE2 on Hetzner for CHEAP! (Part 1).
Some folks don’t want to deploy RKE2, and we don’t want you to feel left out. In this blog we are going to deploy K3s in place of RKE2.
If you want to see why we chose Hetzner for this specific deployment, go check out the previous blog.
Why K3s
K3s is a highly available, certified Kubernetes distribution designed for production workloads in unattended, resource-constrained, remote locations or inside IoT appliances.
There are a few key differences (as of writing) between K3s and RKE2.
- K3s supports ARM processors (like Raspberry Pis).
- K3s is not as focused on FIPS, CIS and other compliance standards as RKE2
- K3s deploys with LocalStorage enabled for Persistent Volumes
- K3s deploys with Traefik ingress controller instead of NGINX ingress controller
Deploying a VM
IMPORTANT Make sure you keep your SSH keys safe, lock the system down with appropriate firewall rules, and keep the OS updated.
So, let’s get started. If you don’t already have a Hetzner account, go sign up here: Hetzner Signup*
Once you are signed up:
- Log in to Hetzner Cloud
- Click on
Defaultproject, or create a new project if you like - Click
Add Serverand select the following options- Location:
Ashburn, VA(or your desired region) - Image:
Ubuntu 20.04 - Type:
StandardandCPX51 - Volume:
None - Network: Create a new one if you like
- Firewalls: Create a new one that allows all access from your IP and only 80/443 from All IPs
- SSH Key: Create a new SSH key to use or use an existing one
- Name:
K3s-Dev
- Location:
- Click
Create & Buy Now
This will provision this new server and provide you and external IP Address that you can use to connect to the node.
Install K3S Kubernetes
Once the node is provisioned, get the IP and login to the cluster using the SSH key you configured.
- In a terminal, run
ssh -i /path/to/key/id_rsa root@YOURSERVERIP
- Update the OS
apt update && apt upgrade -y
- Install K3s:
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -
- Export the kubeconfig file. We can use this file to connect from our local machine using the
kubectlcommand line or Lens
mkdir ~/.kube
cp /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml ~/.kube/config
- Run
kubectl get nodesto verify that the RKE2 node is up and running
root@k3s-dev:~# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k3s-dev Ready control-plane,master 4m34s v1.21.5+k3s2
You now have a single node K3s cluster up and running.
Configure DNS (Optional)
If you would like the cluster to have a DNS name and be able to pull valid Let’s Encrypt keys, you will need to point some DNS names to your cluster. Add the following to you public DNS records for your desired domain. (We use Cloudflare at AB. Reach out if you have questions.)
- rancher.YOURDOMAIN.tld -> IP of your Hetzner Server (This will let you reach the Rancher interface we configure in the next steps)
- *.apps.YOURDOMAIN.tld -> IP of your Hetzner Server (This will let you reach apps running in Kubernetes via NGINX Ingress)
Install Helm
We will use Helm on the Hetzner machine to deploy Rancher (and other applications if you want).
Run the following commands to install Helm:
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh
Deploy Rancher
We can now deploy Rancher 2.6 on the cluster. We will use Rancher as the Management UI for the cluster.
Official documentation: https://rancher.com/docs/rancher/v2.6/en/installation/install-rancher-on-k8s/
- Add the Rancher Stable Helm Repo
helm repo add rancher-stable https://releases.rancher.com/server-charts/stable
- Create a namespace for Rancher
kubectl create namespace cattle-system
- Install
cert-managerfor management of SSL certificates in cluster
# Install cert-manager CRDs
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/jetstack/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.5.1/cert-manager.crds.yaml
# Add the Jetstack Helm repository
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
# Update your local Helm chart repository cache
helm repo update
# Install the cert-manager Helm chart
helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \
--namespace cert-manager \
--create-namespace \
--version v1.5.1
- Install Rancher using Helm. This assumes you have configured DNS to get a valid certificate.
helm install rancher rancher-stable/rancher \
--namespace cattle-system \
--set hostname=rancher.YOURDOMAIN.tld \
--set bootstrapPassword=SUPERSECRETADMINPASSWORD
- Verify rancher deployed successfully
kubectl -n cattle-system rollout status deploy/rancher
- We need to allow Traefik to communicate on 80/433 on our host. To do that, create a file named
traefik.ymland add the following.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: traefik
namespace: kube-system
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
- Apply the the file using
kubectl
kubectl apply -f traefik.yml
- Once Rancher has been fully deployed, visit
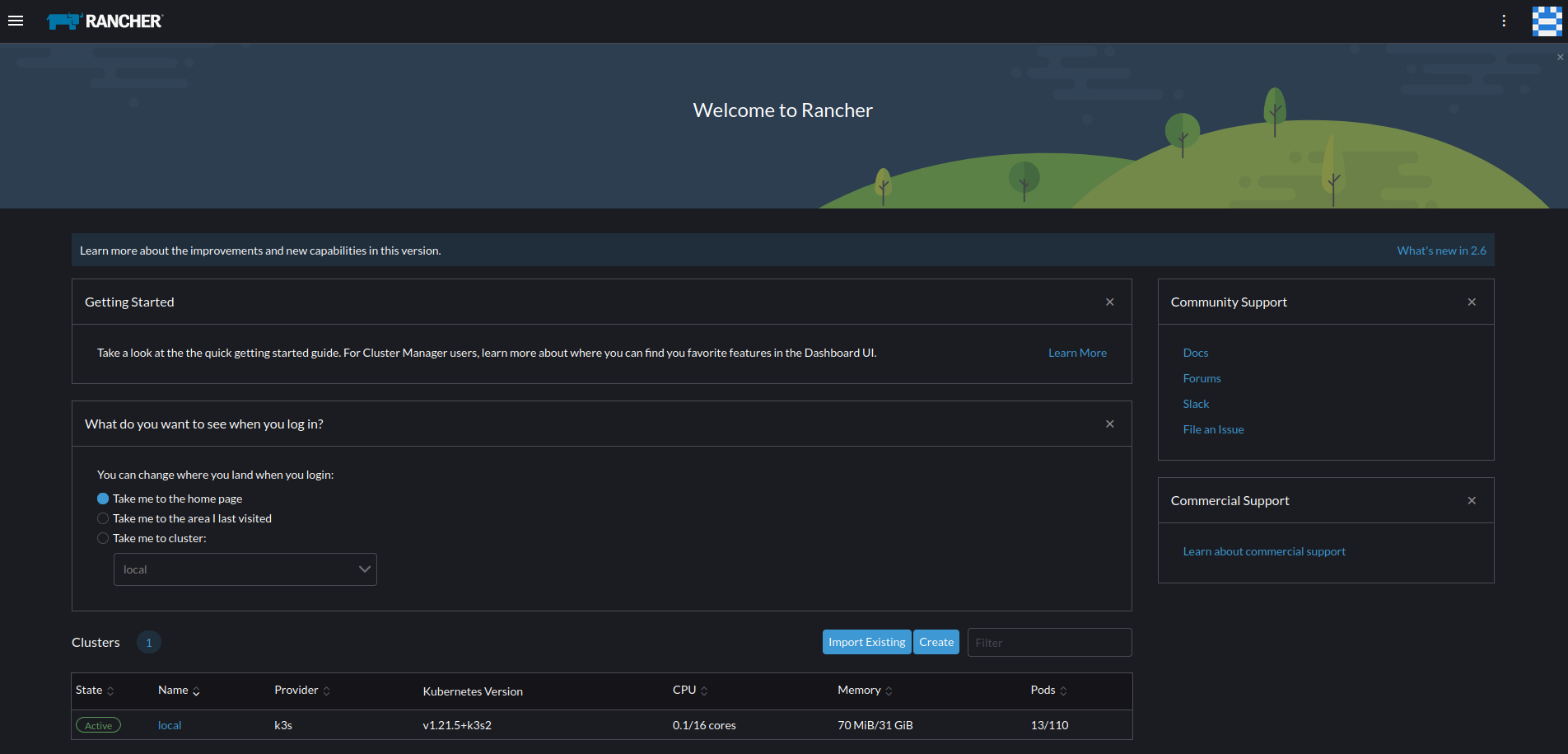
https://rancher.YOURDOMAIN.tldin your browser to login to your Rancher UI and interact with your cluster. Now you should have a fully functioning K3s Single Node Cluster with Rancher Management Interface installed.
Closing
Based on the instructions above, you should now have a powerful K3s Kubernetes cluster you can use for testing and development work.
In the next part of this series, we will go back to RKE2 and install Monitoring and Longhorn for persistent volumes in the cluster.
If you have any questions, please reach out to us at devops@alphabravo.io.
Thanks for reading!
The AB Engineering Team
Website: https://alphabravo.io
Contact Us: https://alphabravo.io/contact-us
Note: Some links included here are affiliate links. If you use the link to sign up, AB may get a small referral credit on our account.
